TL;DR: iOS Safari is more than an inconvenience for developers, it's the fundamental reason interoperability has been stymied in...
Every browser has bugs. But the sheer quantity of things that only fail in Safari is kind of baffling.
Utilizing Contentsquare Digital Experience Monitoring helps gather and rank technical errors on websites. Errors on iOS/Safari are 15% to 45% higher than traffic share, indicating a higher error rate. Yet, none of the dev teams I spoke to planned tests on iOS/Safari.
How to build web pages so they work in HTML first: starting with HTML, extra styles and features, using JavaScript.
Do not build your service as a single-page application (SPA). This is where the loading of pages within your service is handled by JavaScript, rather than the browser.
Single page applications rarely bring benefits and can make the service inaccessible.
Verbatim helps you write on brand.
Use it to measure writing voice as defined by Brand Voice Academy — and understand how every edit impacts the vocabulary, tone, and cadence of your copy.
Adjust your voice to sound any way you want. By having specific measurements in mind, you can edit more precisely to write like anyone or any brand.
Nolan faced a situation that required virtualization. He opted to utilize content-visibility instead for fast immediate gains.
Le justificatif d’identité à usage unique, remplacez vos photocopies de titre d’identité par un document sécurisé pour éviter les fraudes
A live demo to help you get a feel for the INP metric. Start interacting and watch the values update!
Carte des antennes de France métropolitaine et d'outre-mer
skribbl io is a free multiplayer drawing and guessing game. Draw and guess words with your friends and people all around the world! Score the most points and be the winner!
Tips for building Lightning Fast Web Applications!
Through years of trial and error — skipping around radio streams, playing entire collections on shuffle, or repeating certain tracks over and over — we have found that most compelling music for sustained concentration. Music For Programming does not make any profit, nor do any of the episode contributors. The series does not carry any advertising or sponsorship, and never will. The episodes should be considered promotional samples for the artists' work contained within them.
Performance optimizations for the interaction to next paint metric and sharing the learning along the way
While the latency numbers may seem low by themselves, they compound quickly. For example, a network waterfall of depth 3 on a 300ms link leads to a total latency of 900ms.
How much HTML, CSS, and JavaScript can we really afford? More than in years past, but much less than front-end developers are burdening experiences with.
A tool that brings attention and understanding to how color contrast can affect people with different visual impairments.
A creative coding lesson. How the SVG ViewBox works
Recently I made a wall calendar with 12 request waterfalls for a conference, highlighting different web performance issues. This article goes through these waterfalls one by one and explains what they show.
Essentially, there are multiple different ways in which we can attribute a certain task to other tasks or to the party that initiated it.
Those different ways are not always obvious, because for the straightforward case, they all kinda give you the same answer. As a result, it took me a while to wrap my head around their differences, and I’m hoping to save someone some time by outlining them.
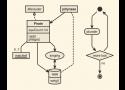
A tool for drawing sassy UML diagrams based on syntax. Provides instant feedback and has a customizable styling.
Submagic is an AI for content creators that generates amazing captions with emojis for short-form content in under 2 minutes. Create your captions and skyrocket your video engagement.
HAR files are JSON-formatted archive files used to log web browser interactions. Developers and IT professionals often use the performance data in HAR files to troubleshoot issues. We want to make it possible to troubleshoot with HAR files without the threat of a stolen session. The HAR File Sanitzer will remove sensitive data using “clientside” logic.